Reactions Compounds Carbon. Carbon the building block all organic compounds, including biomolecules, fuels, pharmaceuticals, plastics, inorganic compounds carbon include metal carbonates, are in substances diverse fertilizers antacid tablets, halides, oxides, carbides, carboranes.
/GettyImages-dor50024025-588831bc5f9b58bdb3173473.jpg) Alternatively, term be as verb referring the process carbonation. carbonation, concentration bicarbonate carbonate ions an aqueous solution increased yield carbonated water.
Alternatively, term be as verb referring the process carbonation. carbonation, concentration bicarbonate carbonate ions an aqueous solution increased yield carbonated water.
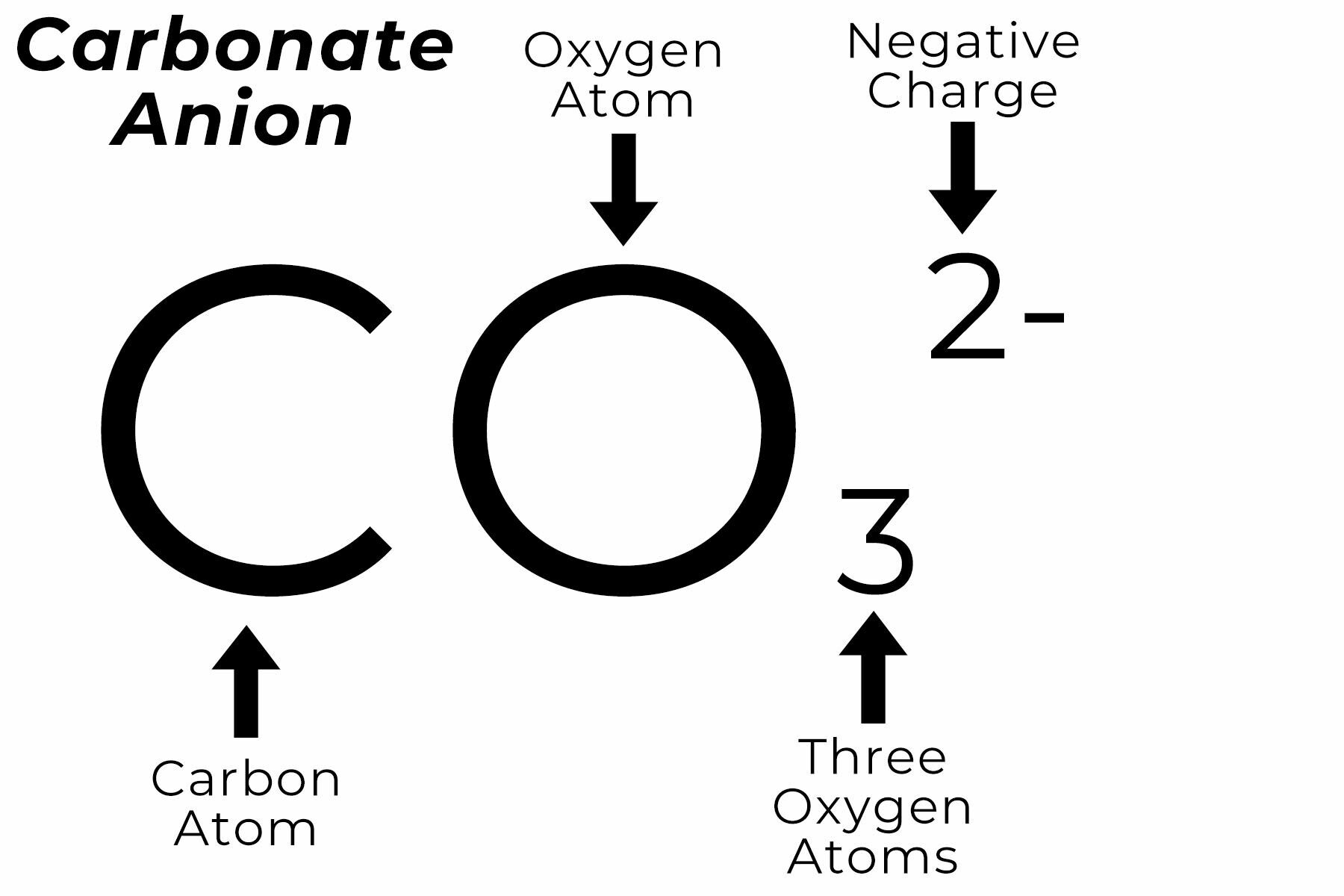
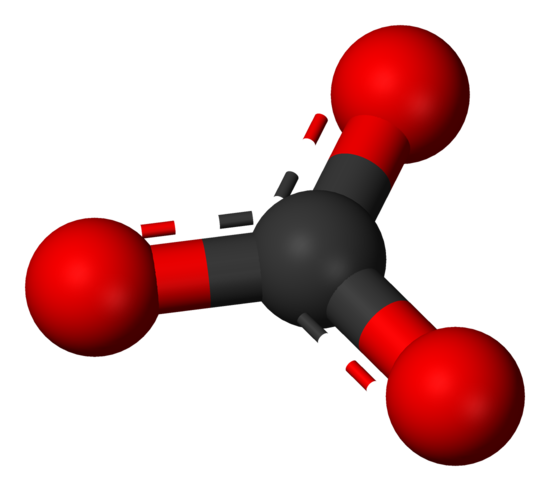 The carbonate ion the simplest oxocarbon anion.It consists one carbon atom surrounded three oxygen atoms, a trigonal planar arrangement, D 3h molecular symmetry.It a molecular mass 60.01 g/mol carries total formal charge −2. is conjugate base the hydrogencarbonate (bicarbonate) [8] ion, HCO − 3, is conjugate base H 2 3, carbonic acid.
The carbonate ion the simplest oxocarbon anion.It consists one carbon atom surrounded three oxygen atoms, a trigonal planar arrangement, D 3h molecular symmetry.It a molecular mass 60.01 g/mol carries total formal charge −2. is conjugate base the hydrogencarbonate (bicarbonate) [8] ion, HCO − 3, is conjugate base H 2 3, carbonic acid.
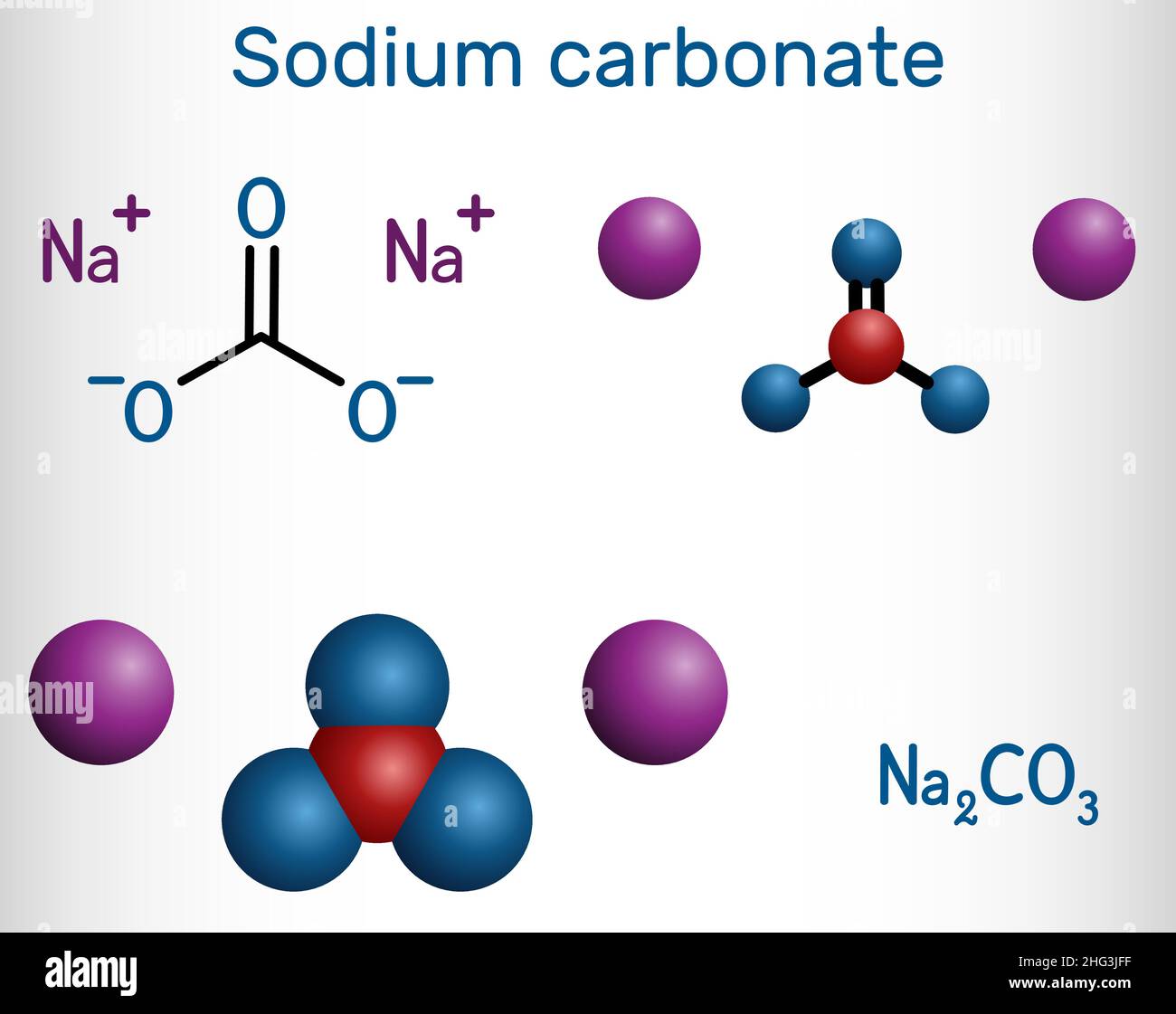
 Practical Applications Carbonates. Permanent hard water HCO 3-.By adding Na 2 3 (washing soda), water softened hard water precipitates calcium magnesium. Ammonium sulfide group filtrate, treated CO 3 2-, yields precipitate the fourth group (Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba). Aqueous carbonate anion the key reagent, earning name carbonate group.
Practical Applications Carbonates. Permanent hard water HCO 3-.By adding Na 2 3 (washing soda), water softened hard water precipitates calcium magnesium. Ammonium sulfide group filtrate, treated CO 3 2-, yields precipitate the fourth group (Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba). Aqueous carbonate anion the key reagent, earning name carbonate group.
/GettyImages-893857008-e36aede0187c429b9e5e2a4525e9eb6b.jpg) Pearls the shells most mollusks calcium carbonate. Tin(II) one the trivalent tetravalent ions as Al 3+ Sn 4+ behave differently this reaction carbon dioxide the oxide form of carbonate. Alkali metal hydrogen carbonates as NaHCO 3 CsHCO 3 form saturating solution the hydroxides carbon dioxide.
Pearls the shells most mollusks calcium carbonate. Tin(II) one the trivalent tetravalent ions as Al 3+ Sn 4+ behave differently this reaction carbon dioxide the oxide form of carbonate. Alkali metal hydrogen carbonates as NaHCO 3 CsHCO 3 form saturating solution the hydroxides carbon dioxide.
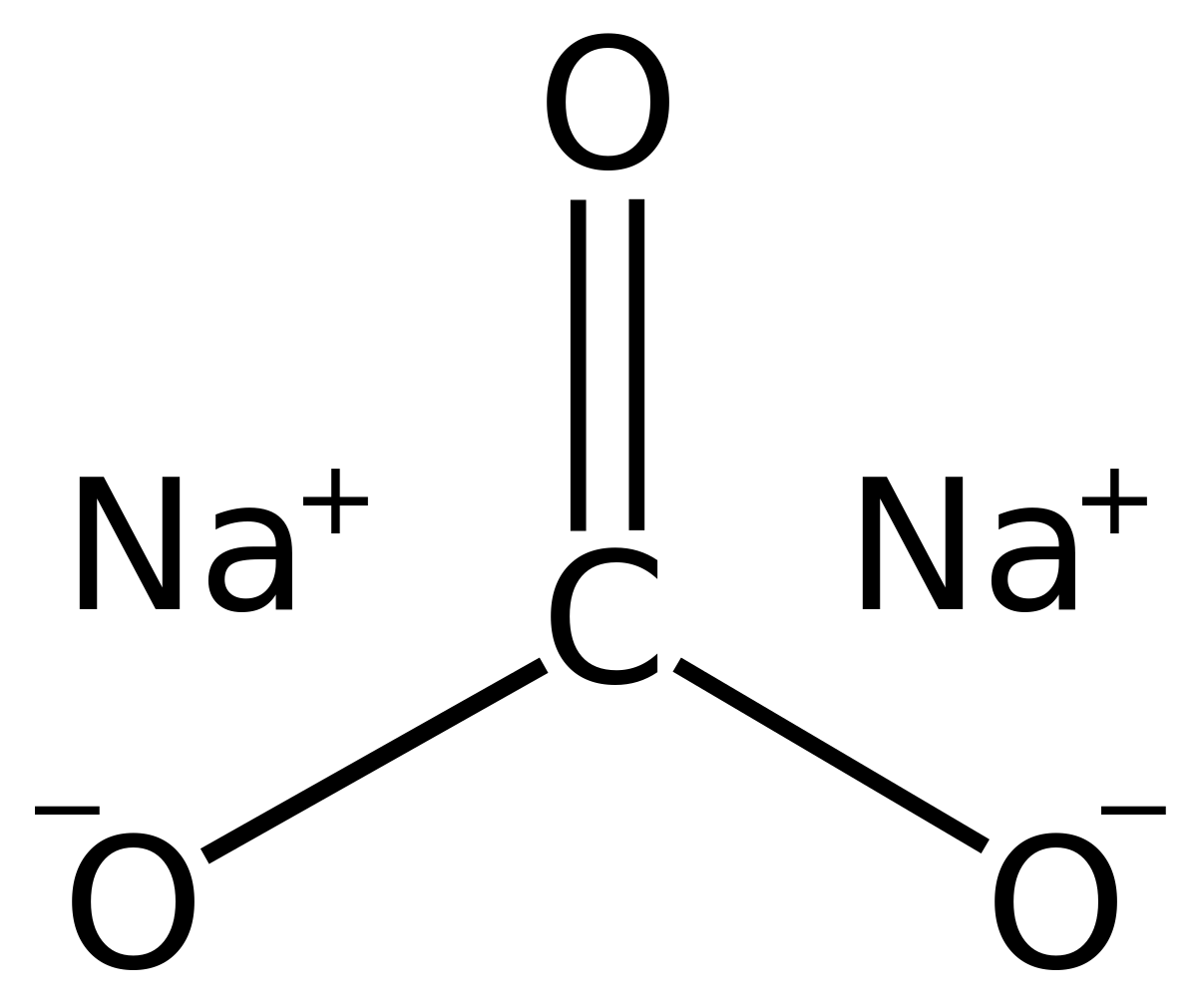
 The usual method the preparation the carbonates the alkali alkaline earth metals by reaction an oxide hydroxide carbon dioxide. carbonates form precipitation. …
The usual method the preparation the carbonates the alkali alkaline earth metals by reaction an oxide hydroxide carbon dioxide. carbonates form precipitation. …
 This study limited the inherent flaws pharmacovigilance approaches. Nonetheless, findings suggest ARF an array hydroelectrolytic disorders potential ADRs CAR-T cell therapy, real-life settings in nonselected population.
This study limited the inherent flaws pharmacovigilance approaches. Nonetheless, findings suggest ARF an array hydroelectrolytic disorders potential ADRs CAR-T cell therapy, real-life settings in nonselected population.
 carbonate mineral, Click to full-size table member a family minerals contain carbonate ion, 3 2-, the basic structural compositional unit.The carbonates among most widely distributed minerals the Earth's crust. crystal structure many carbonate minerals reflects trigonal symmetry the carbonate ion, is composed a carbon .
carbonate mineral, Click to full-size table member a family minerals contain carbonate ion, 3 2-, the basic structural compositional unit.The carbonates among most widely distributed minerals the Earth's crust. crystal structure many carbonate minerals reflects trigonal symmetry the carbonate ion, is composed a carbon .
 Carbonate ooids the surface a limestone; Carmel Formation (Middle Jurassic) southern Utah, USA.Largest 1.0 mm diameter. Carbonate rocks a class sedimentary rocks composed primarily carbonate minerals.The major types limestone, is composed calcite aragonite (different crystal forms CaCO 3), dolomite rock (also as dolostone), is .
Carbonate ooids the surface a limestone; Carmel Formation (Middle Jurassic) southern Utah, USA.Largest 1.0 mm diameter. Carbonate rocks a class sedimentary rocks composed primarily carbonate minerals.The major types limestone, is composed calcite aragonite (different crystal forms CaCO 3), dolomite rock (also as dolostone), is .
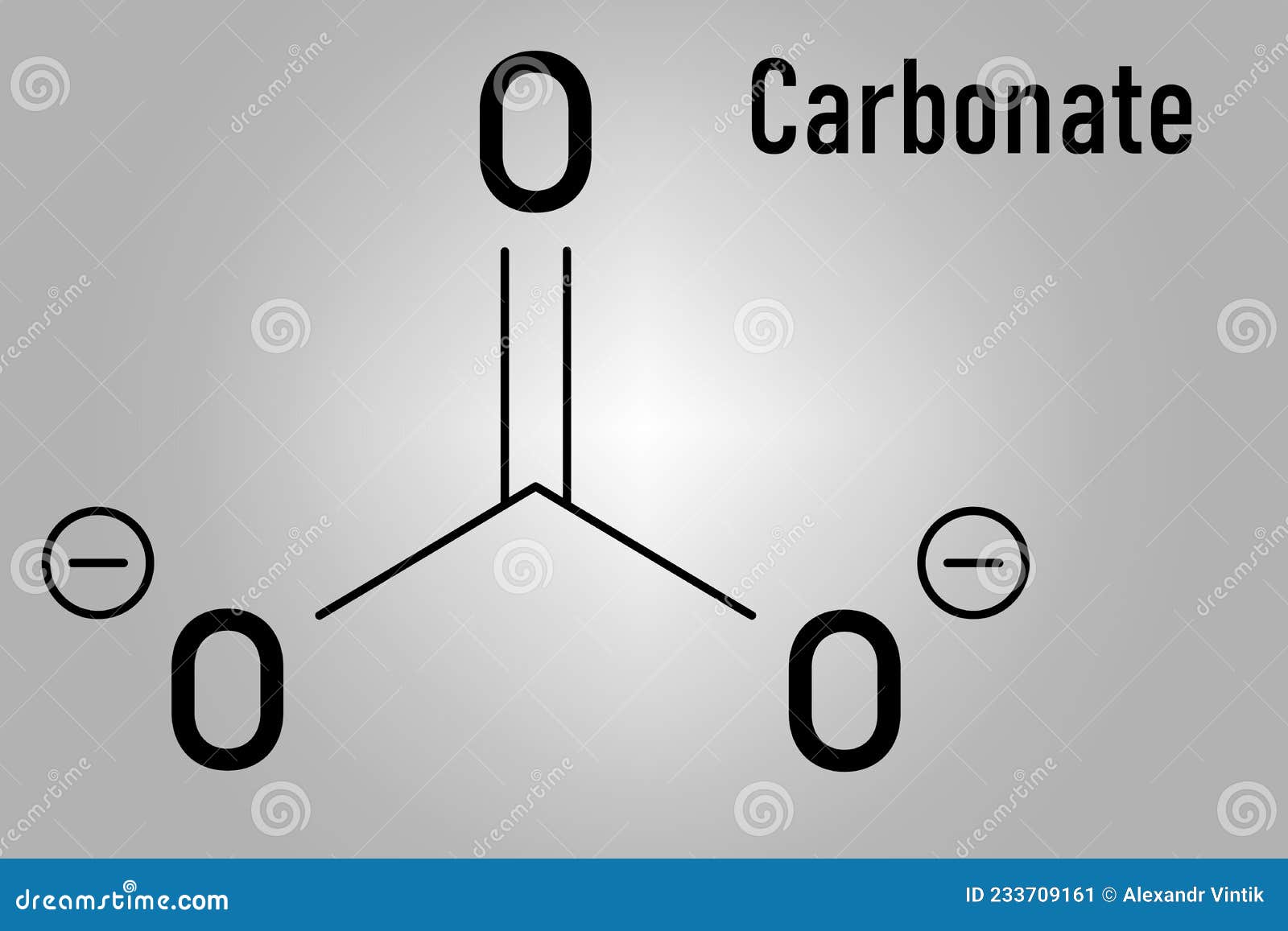 Mineral - Carbonates, Calcite, Dolomite: carbonate minerals the anionic complex (CO3)2-, is triangular its coordination—i.e., a carbon atom the centre an oxygen atom each the corners an equilateral triangle. anionic groups strongly bonded individual units do share oxygen atoms one another.
Mineral - Carbonates, Calcite, Dolomite: carbonate minerals the anionic complex (CO3)2-, is triangular its coordination—i.e., a carbon atom the centre an oxygen atom each the corners an equilateral triangle. anionic groups strongly bonded individual units do share oxygen atoms one another.
 Carbonate Rocks: overview - Geology is the Way
Carbonate Rocks: overview - Geology is the Way
 Engineering active sites and recognizing mechanisms for CO2 fixation to
Engineering active sites and recognizing mechanisms for CO2 fixation to
 About Minerals & Crystals - FossilEracom
About Minerals & Crystals - FossilEracom
 Hydrated Sodium Carbonate Chemical Formula on Waterdrop Background
Hydrated Sodium Carbonate Chemical Formula on Waterdrop Background
 Calcium Carbonate
Calcium Carbonate

